Step 5: The components object (OpenAPI tutorial)
The components object is unique from the other objects in the OpenAPI specification. In components, you store re-usable definitions that might appear in multiple places in your specification document. In our API documentation scenario, we’ll store details for both the parameters and responses object in components.
- Reasons to use the components object
- Objects in components
- Re-using parameters across multiple paths
- Re-using response objects
- Describing a schema
- A way to cheat – automatically generate the schema from JSON using Stoplight
- Using GUI editors to work with the specification code
- View the Appearance in Swagger UI
- The Models section – why it exists, how to hide it
- Security definitions
Reasons to use the components object
Describing the details of your parameters and describing the schema of complex responses can be the most challenging aspects of the OpenAPI spec. Although you can define the parameters and responses directly in the parameters and responses objects, you typically don’t list them there for two reasons:
- You might want to re-use parts of these definitions in other requests or responses. It’s common to have the same parameter or response used in multiple places in an API. Through the
componentsobject, OpenAPI allows you to re-use these same definitions in multiple places. - You might not want to clutter up your
pathsobject with too many parameter and response details, since thepathsobject is already somewhat complex with several levels of objects.
Instead of listing the schema for your requests and responses in the paths object, for more complex schemas (or for schemas that are re-used in multiple operations or paths), you typically use a reference object (referenced with $ref) that points to a specific definition in the components object. (For more details on $ref, see Using $ref.)
Think of the components object like a document appendix where the re-usable details are provided. If multiple parts of your spec have the same schema, you point each of these references to the same object in your components object, and in so doing you single source the content. The components object can even be stored in a separate file if you have a large API and want to organize the information that way. (However, with multiple files, you wouldn’t be able to use the online Swagger Editor to validate the content.)
Objects in components
You can store a lot of different re-usable objects in the components object. The components object can contain these objects:
The properties for each object inside components are the same as they are when used in other parts of the OpenAPI spec. You use a reference pointer ($ref) to point to more details in the components object. $ref stands for reference object and is part of JSON.
Re-using parameters across multiple paths
For the parameters in the previous step, we listed all the details directly in the parameters object. To facilitate re-use of the same parameters in other paths, let’s store the parameters content in components. The code below shows how to make these references:
paths:
/weather:
get:
tags:
- Current Weather Data
summary: "Call current weather data for one location"
description: "Access current weather data for any location on Earth including over 200,000 cities! Current weather is frequently updated based on global models and data from more than 40,000 weather stations."
operationId: CurrentWeatherData
parameters:
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/q'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/id'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lat'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lon'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/zip'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/units'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lang'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/mode'
responses:
200:
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
title: Sample
type: object
properties:
placeholder:
type: string
description: Placeholder description
404:
description: Not found response
content:
text/plain:
schema:
title: Weather not found
type: string
example: Not found
components:
parameters:
q:
name: q
in: query
description: "**City name**. *Example: London*. You can call by city name, or by city name and country code. The API responds with a list of results that match a searching word. For the query value, type the city name and optionally the country code divided by a comma; use ISO 3166 country codes."
schema:
type: string
id:
name: id
in: query
description: "**City ID**. *Example: `2172797`*. You can call by city ID. The API responds with the exact result. The List of city IDs can be downloaded [here](http://bulk.openweathermap.org/sample/). You can include multiple cities in this parameter — just separate them by commas. The limit of locations is 20. *Note: A single ID counts as a one API call. So, if you have city IDs, it's treated as 3 API calls.*"
schema:
type: string
lat:
name: lat
in: query
description: "**Latitude**. *Example: 35*. The latitude coordinate of the location of your interest. Must use with `lon`."
schema:
type: string
lon:
name: lon
in: query
description: "**Longitude**. *Example: 139*. Longitude coordinate of the location of your interest. Must use with `lat`."
schema:
type: string
zip:
name: zip
in: query
description: "**Zip code**. Search by zip code. *Example: 95050,us*. Please note that if the country is not specified, the search uses USA as a default."
schema:
type: string
units:
name: units
in: query
description: '**Units**. *Example: imperial*. Possible values: `standard`, `metric`, and `imperial`. When you do not use the `units` parameter, the format is `standard` by default.'
schema:
type: string
enum: [standard, metric, imperial]
default: "imperial"
lang:
name: lang
in: query
description: '**Language**. *Example: en*. You can use lang parameter to get the output in your language. We support the following languages that you can use with the corresponded lang values: Arabic - `ar`, Bulgarian - `bg`, Catalan - `ca`, Czech - `cz`, German - `de`, Greek - `el`, English - `en`, Persian (Farsi) - `fa`, Finnish - `fi`, French - `fr`, Galician - `gl`, Croatian - `hr`, Hungarian - `hu`, Italian - `it`, Japanese - `ja`, Korean - `kr`, Latvian - `la`, Lithuanian - `lt`, Macedonian - `mk`, Dutch - `nl`, Polish - `pl`, Portuguese - `pt`, Romanian - `ro`, Russian - `ru`, Swedish - `se`, Slovak - `sk`, Slovenian - `sl`, Spanish - `es`, Turkish - `tr`, Ukrainian - `ua`, Vietnamese - `vi`, Chinese Simplified - `zh_cn`, Chinese Traditional - `zh_tw`.'
schema:
type: string
enum: [ar, bg, ca, cz, de, el, en, fa, fi, fr, gl, hr, hu, it, ja, kr, la, lt, mk, nl, pl, pt, ro, ru, se, sk, sl, es, tr, ua, vi, zh_cn, zh_tw]
default: "en"
mode:
name: mode
in: query
description: "**Mode**. *Example: html*. Determines the format of the response. Possible values are `xml` and `html`. If the mode parameter is empty, the format is `json` by default."
schema:
type: string
enum: [json, xml, html]
default: "json"
Replace the existing paths object in the Swagger Editor with the above code sample, include the new components object, and observe that the rendered display still looks the same.
If you get stuck, see the sample OpenAPI spec here for the fully working sample. This will help you spot and troubleshoot indentation or other errors.
Re-using response objects
In Step 4: The paths object, when we described the responses object in the paths object, even with just a simple placeholder, we used a schema object to describe the model for the request or response. The schema refers to the data structure (the fields, values, and hierarchy of the various objects and properties of a JSON or YAML object — see What is a schema?).
Let’s dive deeply into how to use the schema properties to document the responses object. We will also store this content in components so that it can be re-used in other parts of the specification document. If you recall in the previous step (OpenAPI tutorial Step 4: The paths object), the responses object for the weather endpoint looked like this:
paths:
/current:
get:
parameters:
...
responses:
200:
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
title: Sample
type: object
properties:
placeholder:
type: string
description: Placeholder description
404:
description: Not found response
content:
text/plain:
schema:
title: Weather not found
type: string
example: Not found
Now let’s move the schema description for the 200 response into the components object:
paths:
/weather:
get:
tags:
- Current Weather Data
summary: "Call current weather data for one location"
description: "Access current weather data for any location on Earth including over 200,000 cities! Current weather is frequently updated based on global models and data from more than 40,000 weather stations."
operationId: CurrentWeatherData
parameters:
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/q'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/id'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lat'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lon'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/zip'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/units'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lang'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/mode'
responses:
200:
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/200'
404:
description: Not found response
content:
text/plain:
schema:
title: Weather not found
type: string
example: Not found
Then in components/schemas, we’ll define the 200 schema.
Before we describe the response in the components object, it might be helpful to review what the weather response from the OpenWeatherMap API looks like. The JSON response contains multiple nested objects at various levels.
{
"coord": {
"lon": 145.77,
"lat": -16.92
},
"weather": [
{
"id": 803,
"main": "Clouds",
"description": "broken clouds",
"icon": "04n"
}
],
"base": "cmc stations",
"main": {
"temp": 293.25,
"pressure": 1019,
"humidity": 83,
"temp_min": 289.82,
"temp_max": 295.37,
"sea_level": 984,
"grnd_level": 990
},
"wind": {
"speed": 5.1,
"deg": 150
},
"clouds": {
"all": 75
},
"rain": {
"3h": 3
},
"snow": {
"3h": 6
},
"dt": 1435658272,
"sys": {
"type": 1,
"id": 8166,
"message": 0.0166,
"country": "AU",
"sunrise": 1435610796,
"sunset": 1435650870
},
"id": 2172797,
"name": "Cairns",
"cod": 200
}
There are a couple of ways to go about describing this response. You could create a long description that contains all the hierarchy reflected. One challenge with this approach, however, is that it’s difficult to keep all the levels straight. With so many nested objects, it’s dizzying and confusing. Additionally, it’s easy to make mistakes. Worst of all, you can’t re-use the individual objects. This undercuts one of the main reasons for storing this object in components in the first place.
Another approach is to make each object its own entity in the components. Whenever an object contains an object, add a $ref value that points to the new object. This way, the objects remain shallow (rather than having multiple levels of nesting), and you won’t get lost in a sea of confusing sublevels. (If there’s no sub-object, just provide the description directly, without using $ref.
Here’s the description of the 200 response for the weather endpoint. I included the paths tag to maintain some context:
Responses object with components documentation:
paths:
/weather:
get:
tags:
- Current Weather Data
summary: "Call current weather data for one location"
description: "Access current weather data for any location on Earth including over 200,000 cities! Current weather is frequently updated based on global models and data from more than 40,000 weather stations."
operationId: CurrentWeatherData
parameters:
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/q'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/id'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lat'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lon'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/zip'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/units'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lang'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/mode'
responses:
200:
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/200'
404:
description: Not found response
content:
text/plain:
schema:
title: Weather not found
type: string
example: Not found
components:
parameters:
# not shown for the sake of brevity -- see the earlier code block for details
...
schemas:
200:
title: Successful response
type: object
properties:
coord:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Coord'
weather:
type: array
items:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Weather'
description: (more info Weather condition codes)
base:
type: string
description: Internal parameter
example: cmc stations
main:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Main'
visibility:
type: integer
description: Visibility, meter
example: 16093
wind:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Wind'
clouds:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Clouds'
rain:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Rain'
snow:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Snow'
dt:
type: integer
description: Time of data calculation, unix, UTC
format: int32
example: 1435658272
sys:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Sys'
id:
type: integer
description: City ID
format: int32
example: 2172797
name:
type: string
example: Cairns
cod:
type: integer
description: Internal parameter
format: int32
example: 200
Coord:
title: Coord
type: object
properties:
lon:
type: number
description: City geo location, longitude
example: 145.77000000000001
lat:
type: number
description: City geo location, latitude
example: -16.920000000000002
Weather:
title: Weather
type: object
properties:
id:
type: integer
description: Weather condition id
format: int32
example: 803
main:
type: string
description: Group of weather parameters (Rain, Snow, Extreme etc.)
example: Clouds
description:
type: string
description: Weather condition within the group
example: broken clouds
icon:
type: string
description: Weather icon id
example: 04n
Main:
title: Main
type: object
properties:
temp:
type: number
description: 'Temperature. Unit Default: Kelvin, Metric: Celsius, Imperial: Fahrenheit.'
example: 293.25
pressure:
type: integer
description: Atmospheric pressure (on the sea level, if there is no sea_level or grnd_level data), hPa
format: int32
example: 1019
humidity:
type: integer
description: Humidity, %
format: int32
example: 83
temp_min:
type: number
description: 'Minimum temperature at the moment. This is deviation from current temp that is possible for large cities and megalopolises geographically expanded (use these parameter optionally). Unit Default: Kelvin, Metric: Celsius, Imperial: Fahrenheit.'
example: 289.81999999999999
temp_max:
type: number
description: 'Maximum temperature at the moment. This is deviation from current temp that is possible for large cities and megalopolises geographically expanded (use these parameter optionally). Unit Default: Kelvin, Metric: Celsius, Imperial: Fahrenheit.'
example: 295.37
sea_level:
type: number
description: Atmospheric pressure on the sea level, hPa
example: 984
grnd_level:
type: number
description: Atmospheric pressure on the ground level, hPa
example: 990
Wind:
title: Wind
type: object
properties:
speed:
type: number
description: 'Wind speed. Unit Default: meter/sec, Metric: meter/sec, Imperial: miles/hour.'
example: 5.0999999999999996
deg:
type: integer
description: Wind direction, degrees (meteorological)
format: int32
example: 150
Clouds:
title: Clouds
type: object
properties:
all:
type: integer
description: Cloudiness, %
format: int32
example: 75
Rain:
title: Rain
type: object
properties:
3h:
type: integer
description: Rain volume for the last 3 hours
format: int32
example: 3
Snow:
title: Snow
type: object
properties:
3h:
type: number
description: Snow volume for the last 3 hours
example: 6
Sys:
title: Sys
type: object
properties:
type:
type: integer
description: Internal parameter
format: int32
example: 1
id:
type: integer
description: Internal parameter
format: int32
example: 8166
message:
type: number
description: Internal parameter
example: 0.0166
country:
type: string
description: Country code (GB, JP etc.)
example: AU
sunrise:
type: integer
description: Sunrise time, unix, UTC
format: int32
example: 1435610796
sunset:
type: integer
description: Sunset time, unix, UTC
format: int32
example: 1435650870
I’ll explain a bit more in the next sections how to describe the response. In looking at the above code, you may have noticed that not only can you use $ref properties in other parts of your spec but also within components too.
Notice how the schema definition includes an example property for each element? Swagger UI will take this example and use it to dynamically build a full code sample in the Responses section in the Swagger UI output. Thus, you don’t need big chunks of code for the sample responses in your spec. Instead, these sample responses get built automatically from the schema. It’s one of the neat things about Swagger UI. This way, your schema documentation and sample response remain consistent.
Describing a schema
For most of the sections in components, you follow the same object descriptions as detailed in the rest of the spec. However, when describing a schema object, you use standard keywords and terms from the JSON Schema, specifically from the JSON Schema Specification Wright Draft 00.
In other words, you aren’t merely using terms defined by the OpenAPI spec to describe the models for your JSON. As you describe your JSON models (the data structures for input and output objects), the terminology in the OpenAPI spec feeds into the larger JSON definitions and description language for modeling JSON. The OpenAPI’s usage of the JSON Schema is just a subset of the full JSON Schema.
The OpenAPI specification doesn’t attempt to document how to model JSON schemas. This would be redundant with what’s already documented in the JSON Schema site and outside of the scope of the OpenAPI spec. Therefore you might need to consult JSON Schema for more details. (One other helpful tutorial is Advanced Data from API Handyman.)
To describe your JSON objects, you might use the following identifiers:
titlemultipleOfmaximumexclusiveMaximumminimumexclusiveMinimummaxLengthminLengthpatternmaxItemsminItemsuniqueItemsmaxPropertiesminPropertiesrequiredenumtypeallOfoneOfanyOfnotitemspropertiesadditionalPropertiesdescriptionformatdefault
These data types are also available:
integerlongfloatdoublestringbytebinarybooleandatedateTimepassword
When you start documenting your own schema, start by looking in the OpenAPI’s schema object, and then consult the JSON Schema if something isn’t covered.
Additionally, look at some example schemas. You can view 3.0 examples here. I usually find a spec that resembles what I’m trying to represent and mimic the same properties and structure.
The schema object in 3.0 differs slightly from the schema object in 2.0 — see this post on Nordic APIs for some details on what’s new. However, example schemas from 2.0 specs (which are a lot more abundant online) would probably also be helpful as long as you just look at the schema definitions and not the rest of the spec.
A way to cheat – automatically generate the schema from JSON using Stoplight
Describing a JSON response can be complicated and confusing. Fortunately, there’s a somewhat easy workaround. To be honest, this is the approach I use when I’m documenting JSON responses. Download Stoplight and use the Generate JSON feature to have Stoplight automatically create the OpenAPI schema description. Here’s a short (silent) video showing how to do this:
Basically, you copy the JSON response you want to document into the Stoplight Editor. Then you click Generate JSON. Go into the code view and copy the JSON. Then convert the JSON to YAML using an online converter. For more details, see Stoplight — visual modeling tools for creating your OpenAPI spec.
The only catch is that Stoplight uses OpenAPI 2.0, not 3.0. You might need to use API Transformer to convert the 2.0 schema output to 3.0. Even so, this approach can save you a lot of time.
Using GUI editors to work with the specification code
At this point, you’re probably thinking how impractical and error-prone it’s going to be as you work directly in the YAML code like this. For this reason, several companies have developed GUI editors to make it easier to work with the specification code. In particular, check out Stoplight, which provides an editor that lets you toggle between code and a GUI display. Smartbear also offers SwaggerHub, which doesn’t necessarily provide a GUI but which gives you inline commenting and versioning tools. (Note that both Stoplight and Smartbear are sponsors of the site, but I would mention them here anyway.)
View the Appearance in Swagger UI
Copy the following code and paste it into the Swagger Editor below your openapi, info and servers objects:
paths:
/weather:
get:
tags:
- Current Weather Data
summary: "Call current weather data for one location"
description: "Access current weather data for any location on Earth including over 200,000 cities! Current weather is frequently updated based on global models and data from more than 40,000 weather stations."
operationId: CurrentWeatherData
parameters:
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/q'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/id'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lat'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lon'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/zip'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/units'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/lang'
- $ref: '#/components/parameters/mode'
responses:
200:
description: Successful response
content:
application/json:
schema:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/200'
404:
description: Not found response
content:
text/plain:
schema:
title: Weather not found
type: string
example: Not found
components:
parameters:
q:
name: q
in: query
description: "**City name**. *Example: London*. You can call by city name, or by city name and country code. The API responds with a list of results that match a searching word. For the query value, type the city name and optionally the country code divided by a comma; use ISO 3166 country codes."
schema:
type: string
id:
name: id
in: query
description: "**City ID**. *Example: `2172797`*. You can call by city ID. The API responds with the exact result. The List of city IDs can be downloaded [here](http://bulk.openweathermap.org/sample/). You can include multiple cities in this parameter — just separate them by commas. The limit of locations is 20. *Note: A single ID counts as a one API call. So, if you have city IDs, it's treated as 3 API calls.*"
schema:
type: string
lat:
name: lat
in: query
description: "**Latitude**. *Example: 35*. The latitude coordinate of the location of your interest. Must use with `lon`."
schema:
type: string
lon:
name: lon
in: query
description: "**Longitude**. *Example: 139*. Longitude coordinate of the location of your interest. Must use with `lat`."
schema:
type: string
zip:
name: zip
in: query
description: "**Zip code**. Search by zip code. *Example: 95050,us*. Please note that if the country is not specified, the search uses USA as a default."
schema:
type: string
units:
name: units
in: query
description: '**Units**. *Example: imperial*. Possible values: `standard`, `metric`, and `imperial`. When you do not use the `units` parameter, the format is `standard` by default.'
schema:
type: string
enum: [standard, metric, imperial]
default: "imperial"
lang:
name: lang
in: query
description: '**Language**. *Example: en*. You can use lang parameter to get the output in your language. We support the following languages that you can use with the corresponded lang values: Arabic - `ar`, Bulgarian - `bg`, Catalan - `ca`, Czech - `cz`, German - `de`, Greek - `el`, English - `en`, Persian (Farsi) - `fa`, Finnish - `fi`, French - `fr`, Galician - `gl`, Croatian - `hr`, Hungarian - `hu`, Italian - `it`, Japanese - `ja`, Korean - `kr`, Latvian - `la`, Lithuanian - `lt`, Macedonian - `mk`, Dutch - `nl`, Polish - `pl`, Portuguese - `pt`, Romanian - `ro`, Russian - `ru`, Swedish - `se`, Slovak - `sk`, Slovenian - `sl`, Spanish - `es`, Turkish - `tr`, Ukrainian - `ua`, Vietnamese - `vi`, Chinese Simplified - `zh_cn`, Chinese Traditional - `zh_tw`.'
schema:
type: string
enum: [ar, bg, ca, cz, de, el, en, fa, fi, fr, gl, hr, hu, it, ja, kr, la, lt, mk, nl, pl, pt, ro, ru, se, sk, sl, es, tr, ua, vi, zh_cn, zh_tw]
default: "en"
mode:
name: mode
in: query
description: "**Mode**. *Example: html*. Determines the format of the response. Possible values are `xml` and `html`. If the mode parameter is empty, the format is `json` by default."
schema:
type: string
enum: [json, xml, html]
default: "json"
schemas:
200:
title: Successful response
type: object
properties:
coord:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Coord'
weather:
type: array
items:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Weather'
description: (more info Weather condition codes)
base:
type: string
description: Internal parameter
example: cmc stations
main:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Main'
visibility:
type: integer
description: Visibility, meter
example: 16093
wind:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Wind'
clouds:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Clouds'
rain:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Rain'
snow:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Snow'
dt:
type: integer
description: Time of data calculation, unix, UTC
format: int32
example: 1435658272
sys:
$ref: '#/components/schemas/Sys'
id:
type: integer
description: City ID
format: int32
example: 2172797
name:
type: string
example: Cairns
cod:
type: integer
description: Internal parameter
format: int32
example: 200
Coord:
title: Coord
type: object
properties:
lon:
type: number
description: City geo location, longitude
example: 145.77000000000001
lat:
type: number
description: City geo location, latitude
example: -16.920000000000002
Weather:
title: Weather
type: object
properties:
id:
type: integer
description: Weather condition id
format: int32
example: 803
main:
type: string
description: Group of weather parameters (Rain, Snow, Extreme etc.)
example: Clouds
description:
type: string
description: Weather condition within the group
example: broken clouds
icon:
type: string
description: Weather icon id
example: 04n
Main:
title: Main
type: object
properties:
temp:
type: number
description: 'Temperature. Unit Default: Kelvin, Metric: Celsius, Imperial: Fahrenheit.'
example: 293.25
pressure:
type: integer
description: Atmospheric pressure (on the sea level, if there is no sea_level or grnd_level data), hPa
format: int32
example: 1019
humidity:
type: integer
description: Humidity, %
format: int32
example: 83
temp_min:
type: number
description: 'Minimum temperature at the moment. This is deviation from current temp that is possible for large cities and megalopolises geographically expanded (use these parameter optionally). Unit Default: Kelvin, Metric: Celsius, Imperial: Fahrenheit.'
example: 289.81999999999999
temp_max:
type: number
description: 'Maximum temperature at the moment. This is deviation from current temp that is possible for large cities and megalopolises geographically expanded (use these parameter optionally). Unit Default: Kelvin, Metric: Celsius, Imperial: Fahrenheit.'
example: 295.37
sea_level:
type: number
description: Atmospheric pressure on the sea level, hPa
example: 984
grnd_level:
type: number
description: Atmospheric pressure on the ground level, hPa
example: 990
Wind:
title: Wind
type: object
properties:
speed:
type: number
description: 'Wind speed. Unit Default: meter/sec, Metric: meter/sec, Imperial: miles/hour.'
example: 5.0999999999999996
deg:
type: integer
description: Wind direction, degrees (meteorological)
format: int32
example: 150
Clouds:
title: Clouds
type: object
properties:
all:
type: integer
description: Cloudiness, %
format: int32
example: 75
Rain:
title: Rain
type: object
properties:
3h:
type: integer
description: Rain volume for the last 3 hours
format: int32
example: 3
Snow:
title: Snow
type: object
properties:
3h:
type: number
description: Snow volume for the last 3 hours
example: 6
Sys:
title: Sys
type: object
properties:
type:
type: integer
description: Internal parameter
format: int32
example: 1
id:
type: integer
description: Internal parameter
format: int32
example: 8166
message:
type: number
description: Internal parameter
example: 0.0166
country:
type: string
description: Country code (GB, JP etc.)
example: AU
sunrise:
type: integer
description: Sunrise time, unix, UTC
format: int32
example: 1435610796
sunset:
type: integer
description: Sunset time, unix, UTC
format: int32
example: 1435650870
securitySchemes:
app_id:
type: apiKey
description: API key to authorize requests.
name: appid
in: query
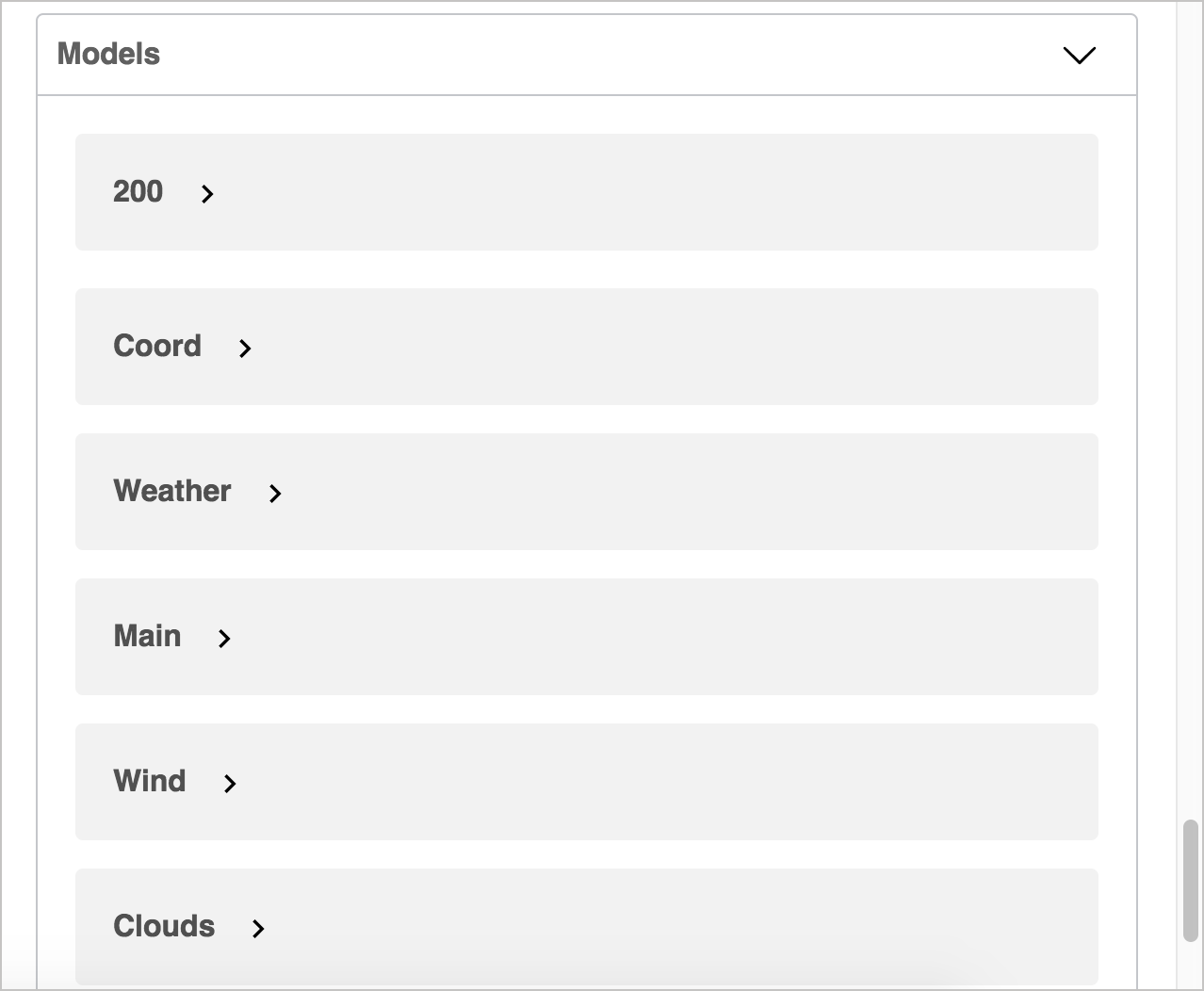
You should see the following populate in the Swagger UI display:
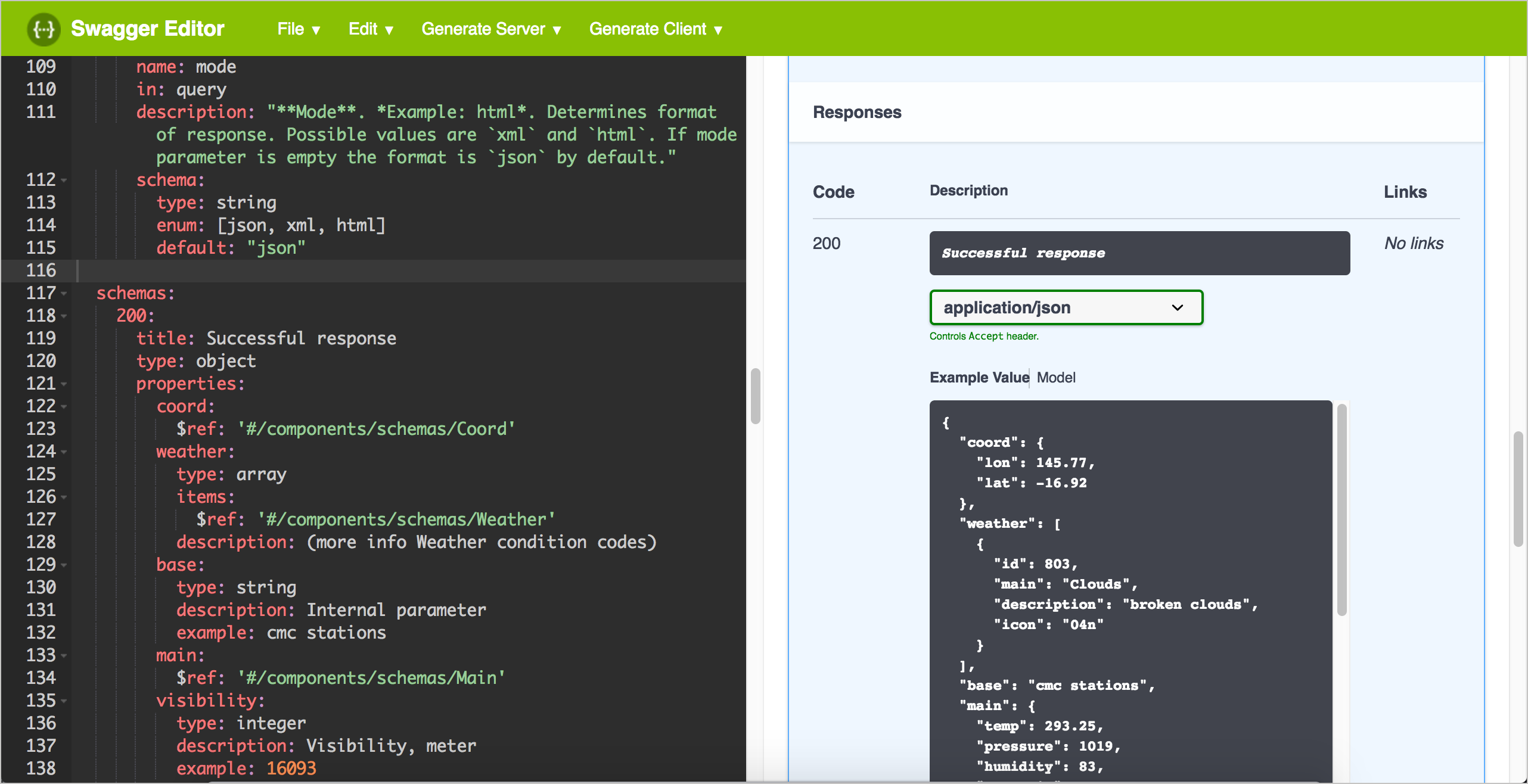
In the Response section, observe how the Example Value code has been dynamically built from the example values in the schema to show a sample response.
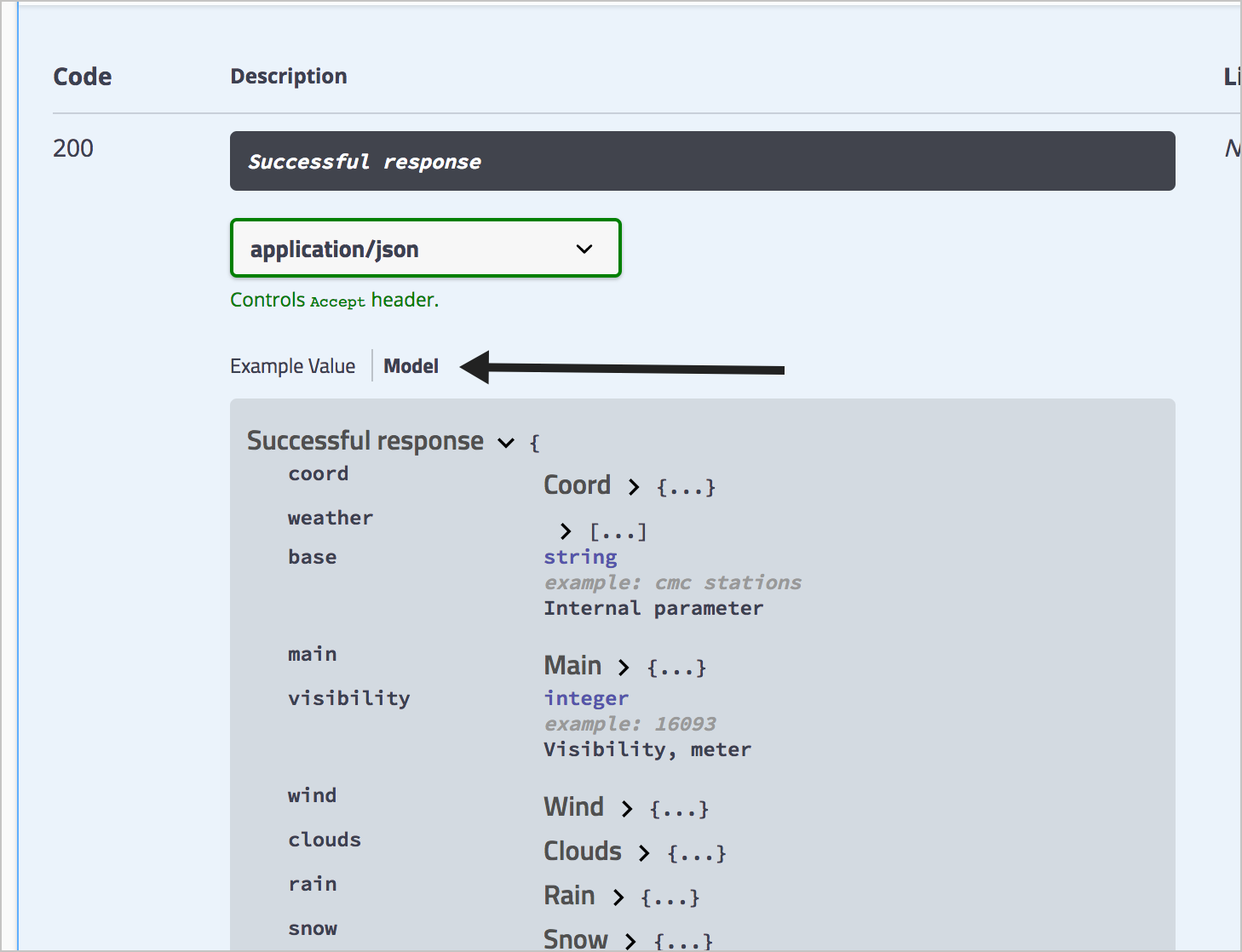
Also, click the Model link to see how the descriptions of each element appear in an expandable/collapsible way:
The Models section – why it exists, how to hide it
You’ll also notice another “Models” section below all the other paths:
By default, Swagger UI displays each object in components in a section called “Models” at the end of your Swagger UI display. If you consolidate all schemas into a single object, without using the $ref property to point to new objects, you will see just one object in Models. If you split out the objects, then you see each object listed separately, including the object that contains all the references.
Because I want to re-use objects, I’m going to define each object in components separately. As a result, the Models section looks like this:
Why is there a Models section here? Apparently, it was added by popular request because the online Swagger Editor showed the display, and many users asked for it to be incorporated into Swagger UI.
You don’t need this Models section in Swagger UI because both the request and response sections of Swagger UI provide a “Model” link that lets the user toggle to this view.
To hide the Models section, you can add the parameter defaultModelsExpandDepth: -1 parameter in your Swagger UI project. I provide a Swagger UI tutorial in an upcoming section in this course, with details about the Swagger UI parameters where you could configure this parameter.
Security definitions
The components object also contains a securitySchemes object that defines the authorization method used with each path. Rather than dive into the security configuration details here, I explore security in Step 6: The security object.
46/145 pages complete. Only 99 more pages to go.