API rate limiting and thresholds
Rate limits determine how frequently you can call a particular endpoint. Usually, companies have different tiers (for example, free versus pro) and licenses (open-source, business, commercial) corresponding to different capabilities or rate limits with the API.
What to cover with rate limiting
Companies with APIs make money by charging for access to the API, but they usually distinguish between low usage and high usage, often making the low usage options free so that developers can explore and experiment with the API. With the sample OpenWeatherMap Weather API that we’ve been using in this course, you can see where the pricing tier begins:
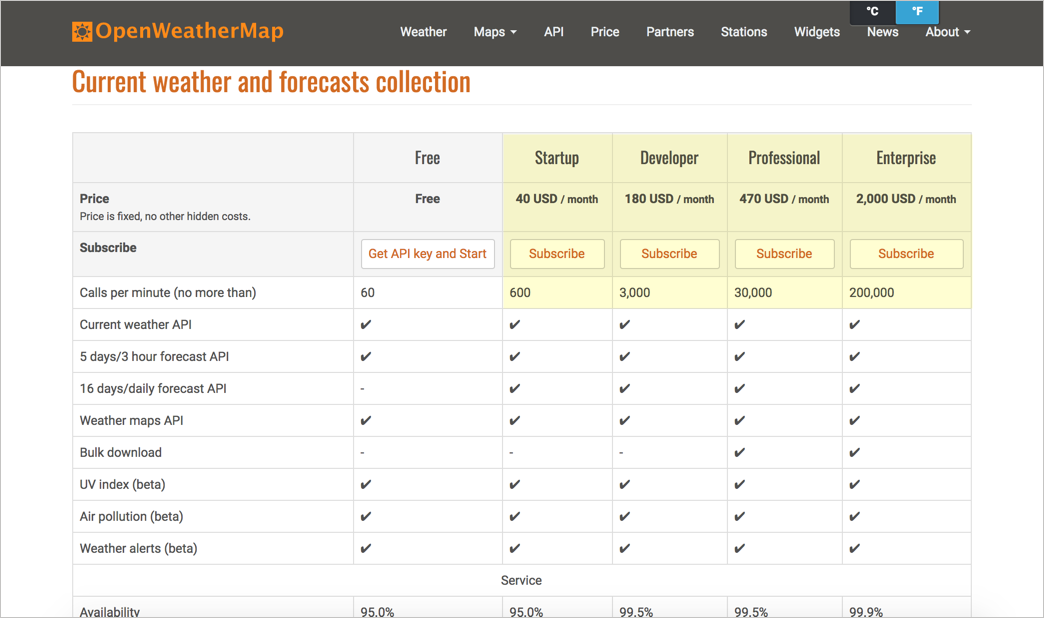
If your site has hundreds of thousands of visitors a day, and with each page reload calls an API endpoint, you want to be sure the API can support that kind of traffic.
Pricing related to rate limiting is probably information that’s within the marketing domain rather than documentation domain. However, developers will still want to know a few key behaviors around the rate-limiting thresholds. For example:
- When you exceed the threshold, do your calls get throttled with slower responses?
- Do you get overcharges for every extra call?
- If you exceed the limit, do the responses return a particular status code (if so, which one)?
Also, when developers implement the code into their applications, how are they handling situations where the API doesn’t respond due to rate limit violations? Are there conditions and checks to handle these throttled scenarios? Does the widget (or whatever might be implementing the API) freeze or hang, display empty or crash?

Examples rate limiting sections
Here are a few examples of rate limiting sections in API documentation.
GitHub
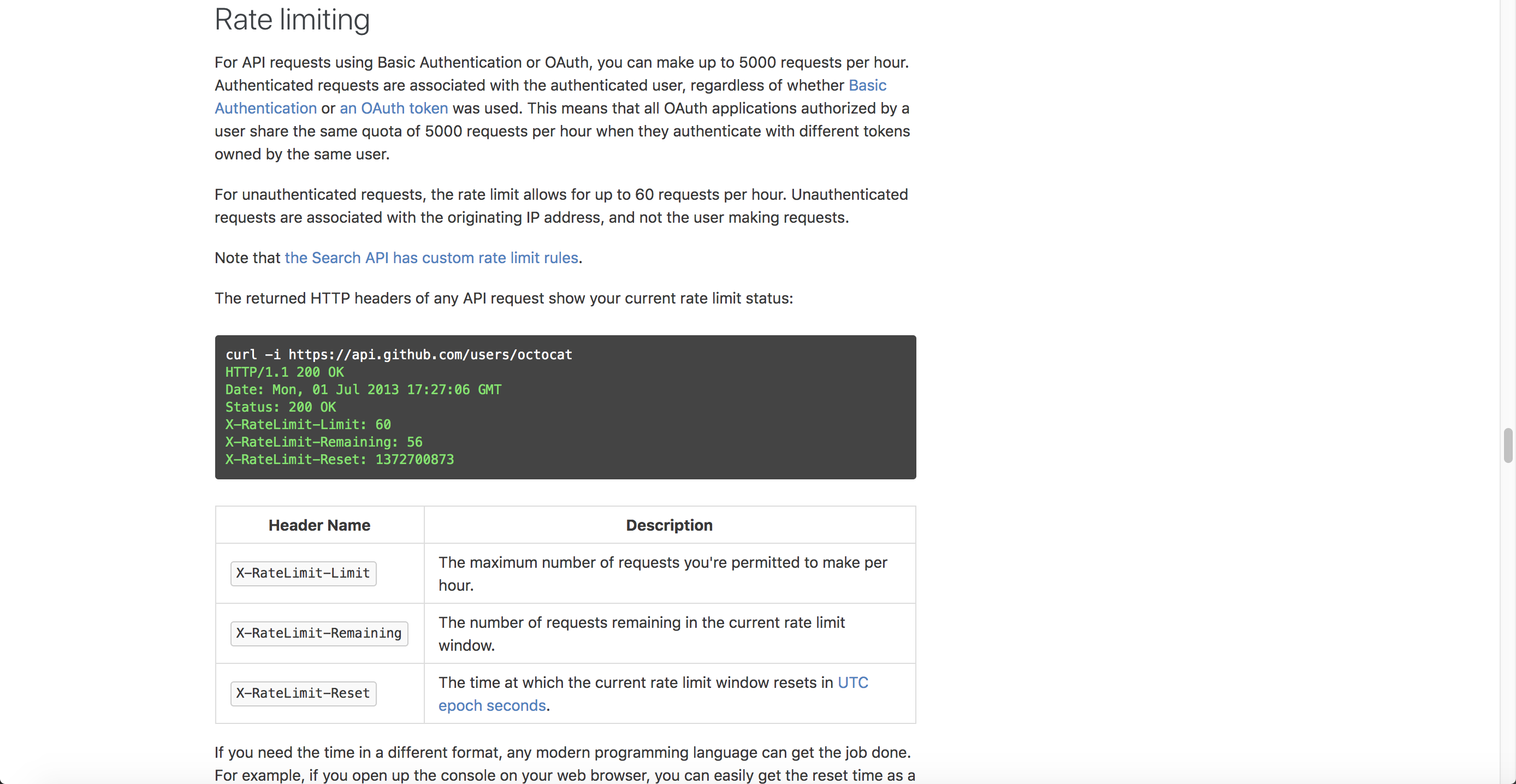
GitHub’s documentation explains rate limits for authenticated versus unauthenticated requests, the header returned, the meaning of the rate-limiting titles (X-RateLimit-Limit, X-RateLimit-Remaining, and X-RateLimit-Reset), how to check your current usage, how to increase rate limits for a specific application, what happens when rate limits are abused, and more.
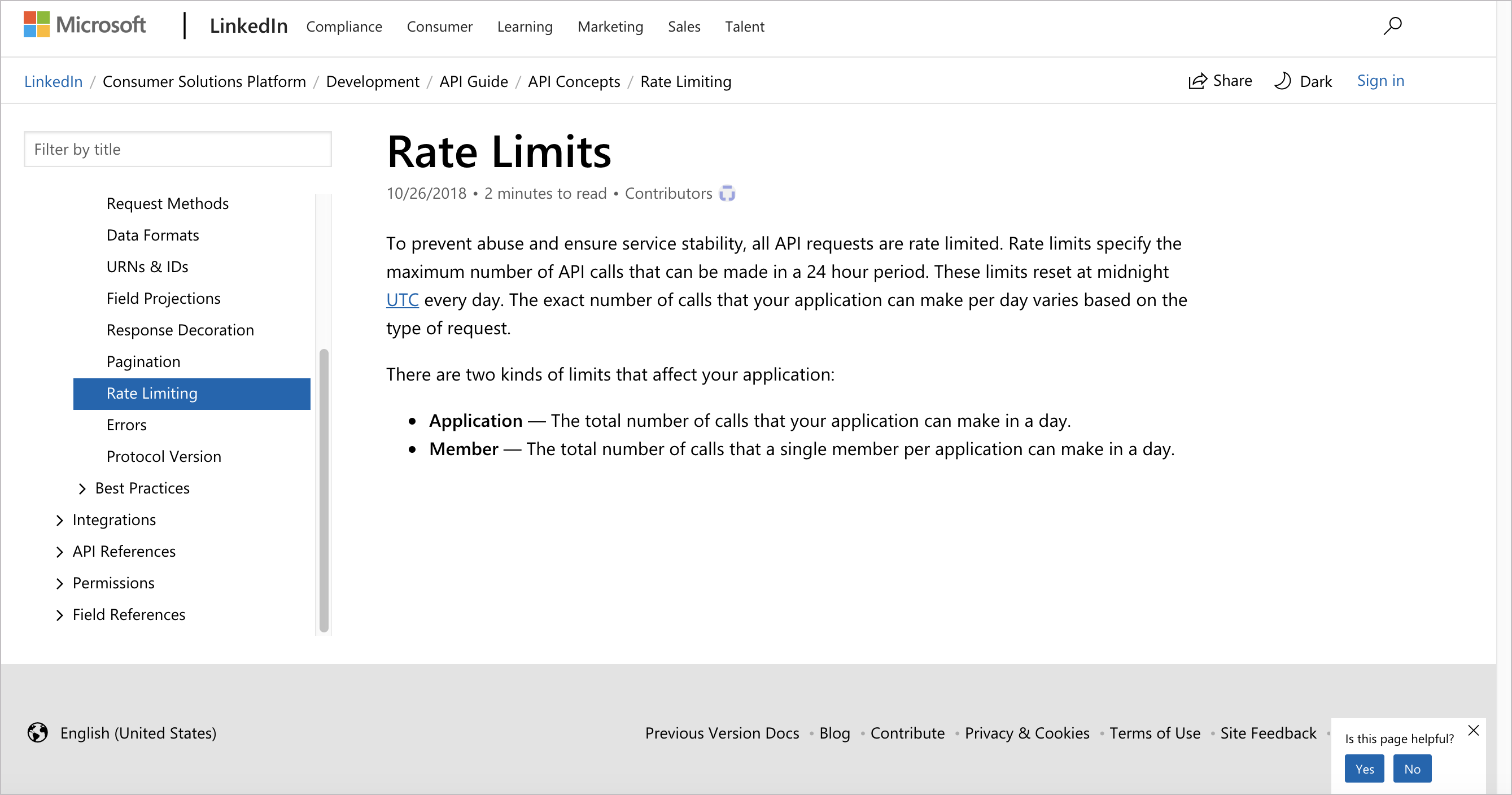
Linkedin’s rate limiting documentation explains that different API endpoints have different limits. There are three different types of throttling: Application throttling, User throttling, and Developer throttling. Their documentation also explains the time zone used to track the day’s beginning and end.
Bitly
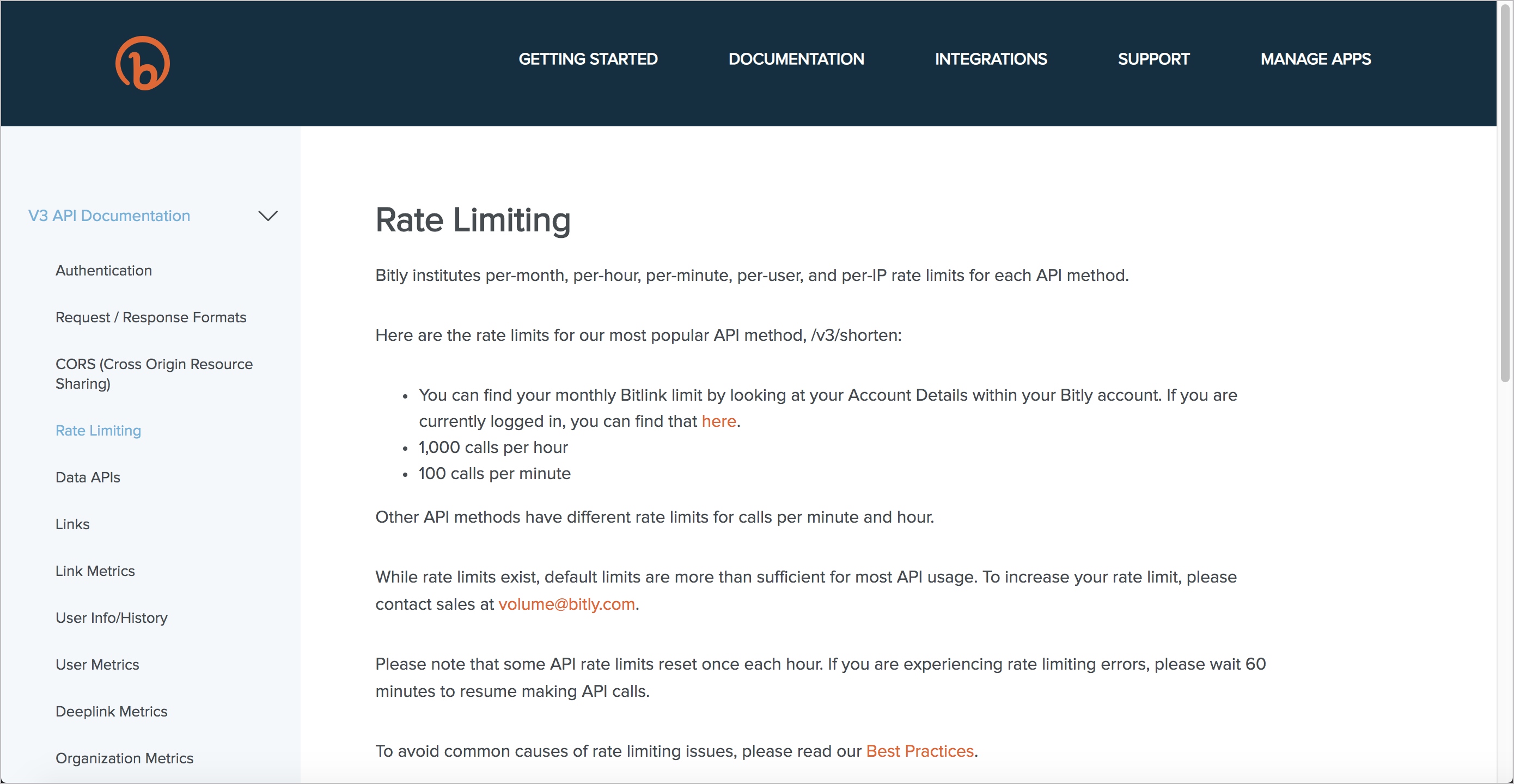
Bitly provides basic information on the page above but also links to best practices for avoiding rate-limiting issues. These best practices include tips such as caching, security issues, long page loads, batch processing, high-volume requests, URL encoding, and more.
By looking at these examples, you can see that while rate limiting might seem like a straightforward topic, there are layers of depth and complexity to cover. The relevance of the topic depends on your API and the rate-limiting policies your company sets, but this information cannot be entirely offloaded to Marketing to handle. So much of the information around rate limiting directly affects development.
Activity with rate limits
With the open-source project you identified, identify the information about rate limits with the API. Answer the following questions:
- Does the API have rate limits?
- What happens if users exceed the rate limits?
- What status codes are sent if rate limits are exceeded?
- What kind of rate limits exist with the free (or development) tiers of the API?
75/145 pages complete. Only 70 more pages to go.
